
For example, when the engineering BOM defines each sub-assembly separately, the manufacturing BOM will not define the sub-assemblies separately, but only includes the total material requirements for making the sub-assemblies. For example, when the engineering BOM states that Part A will be used, the manufacturing BOM will say that Part A alternative will be used, because, in reality, the shop-floor uses another material. For example, while the engineering BOM states that a 1-meter stick contains 1-meter of a stick, the manufacturing BOM will say that making of a 1-meter stick consumes 1.2 meters of a stick (incl. This kind of bill of materials is used for production planning in an MRP system, where it's necessary to know the gross number of all materials for planning purposes and inventory picking. The assembly structure is often simplified, if possible, even to a single level.
For example, when materials planning for some material is not necessary, or that level of detail, each sub-assembly planning separately, is not necessary.
Some structures and parts might even not be included. The manufacturing BOM or MRP BOM takes into account wastage and other consumables used in production considers the material requirements planning goals, and corresponds to the process of how the product is actually manufactured.This kind of bill of materials is a typical output of a CAD program and is used by the engineering department as the technical specification.
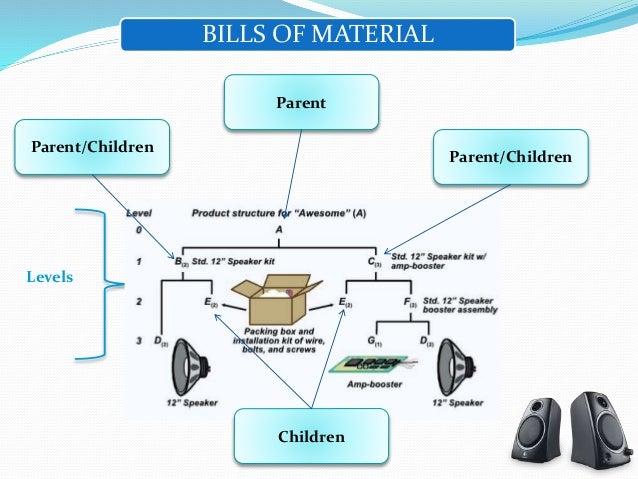
Often does not reflect everything that is actually consumed during production. The engineering BOM states exact quantities of parts or ingredients inside the product, including the detailed assembly structure of the product.This is also known by the terms " phantom assembly" or " phantom BOM".įor example, a Bill of Materials of a table:Īn "engineering BOM" is not always the same as the "manufacturing BOM" or "MRP BOM": If a sub-assembly does not have a routing, then it is considered as a collection of parts in a multi-level Manufacturing Order.it could have multi-level sub-assemblies, where each sub-assembly has its own BOM and even a routing.A product can have a single-level assembly structure, where it is directly made from raw materials, or.The bill of materials usually consists of several parts, and it could also include other consumables that don't make up the product (e.g. When a manufacturing order is created, the BOM is multiplied by the order quantity to calculate the total material requirements. for process manufacturing, like food, pharmaceutics, etc., it is the formula or recipe which lists the quantities of ingredients per unit of product.for discrete manufacturing, like electronics, industrial equipment, etc., it's the list of parts.In MRPeasy, a Bill of Materials (BOM) is the list of materials that are needed to create one unit of product.
#FINALE INVENTORY BOM HOW TO#
#FINALE INVENTORY BOM UPDATE#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
